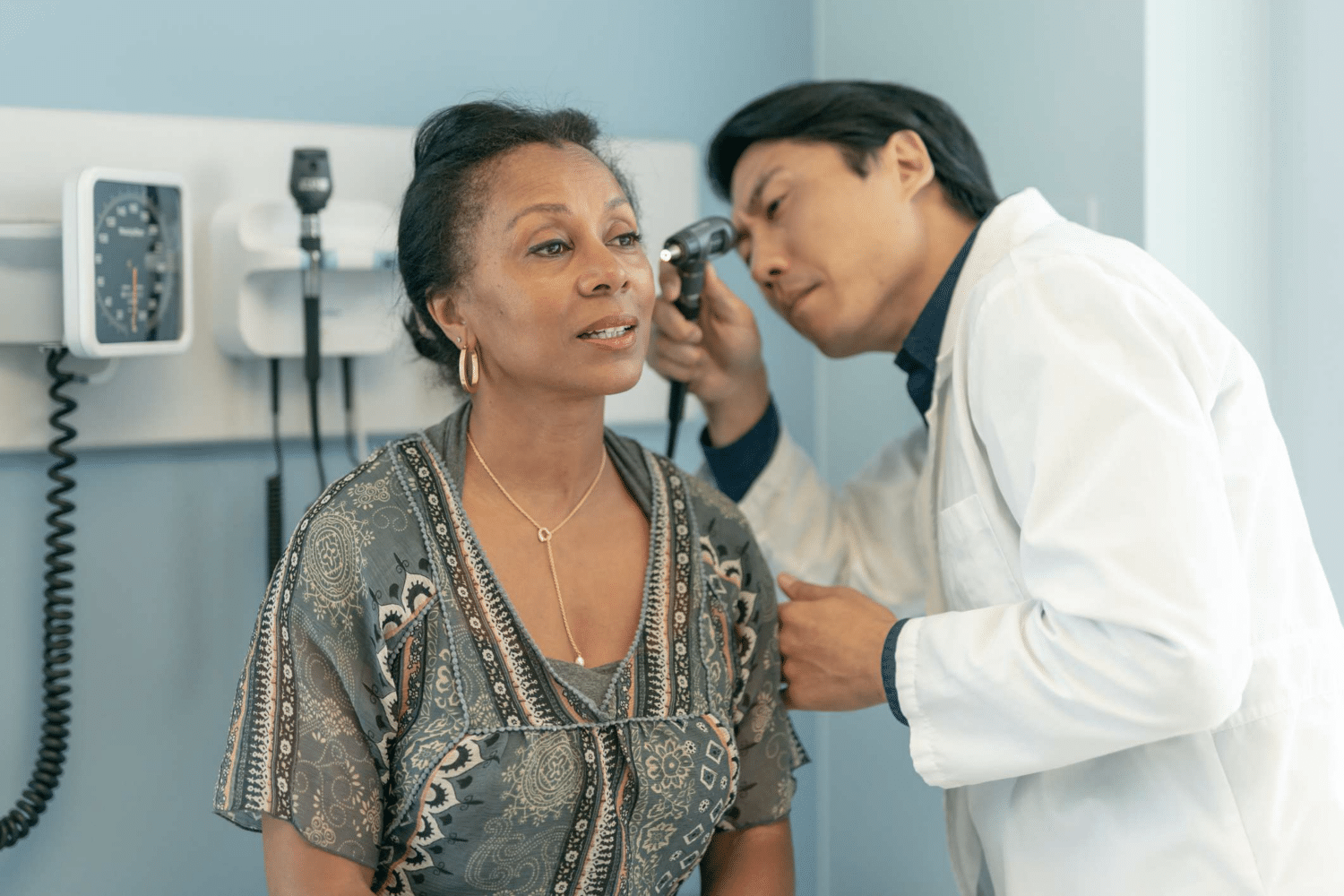
Hearing is a critical sense that enables us to communicate, stay connected with the world, and enjoy life’s great sounds. American Hearing Centers in New Jersey are dedicated to addressing your hearing health. Do I need a hearing test? How often should it be done? These are common questions we hear from patients frequently. Exploring the importance of these tests and the guidance we provide based on the results are essential to helping you make informed decisions about your ear care.
The Importance of Hearing Health
Listening is integral to our daily lives—whether conversing with loved ones, enjoying music, or receiving important information. Neglecting your ear health can lead to decreased quality of life and missed connections. More importantly, untreated hearing loss is directly related to numerous health concerns, including:
- Diabetes
- Dementia
- Cognitive Decline
- Kidney Disease
- Heart Disease
- Tinnitus
- Risk of Falls
- Depression
Who Is a Candidate for Hearing Tests?
A hearing test evaluation should be a part of everyone’s overall health care plan. Healthy adults should have a hearing test about once every seven to 10 years up until age 50. Between 50 and 65, a test should be done every three to five years. After 65, hearing tests should be done about every two years and become a yearly exam for anyone 75 and older. Since hearing loss commonly occurs suddenly over time, it’s vital to keep up with tests to detect early signs, such as difficulty hearing certain sounds, pitches, or frequencies. Individuals who work in loud environments, such as industrial settings or nightclubs, should get tested more frequently since they’re at risk for noise-induced hearing loss and tinnitus.
What Types of Hearing Loss Testing Are Available?
Hearing tests are painless and can provide a wealth of information about your ear health, with results available immediately, uncovering the type and severity of the impairment. The different tests your hearing care provider might perform include:
- Pure-Tone Audiometry – Measures your ability to hear a range of pitches at different volumes.
- Speech Audiometry – Evaluates your ability to hear and understand speech.
- Tympanometry – Tests how well your middle ear is functioning.
- Bone Conduction Testing – Bypasses the outer and middle ear to distinguish between sensorineural and conductive hearing loss.
Signs of Potential Hearing Loss
Knowing the signs of hearing loss is the first step in taking action. Common indicators include:
- Difficulty following conversations, especially in noisy environments.
- Frequently asking others to repeat themselves.
- Turning up the volume on devices louder than what others require.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s a good reason to consider a hearing test and professional advice.
Understanding the Different Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is broadly categorized into three types, each with distinct causes and implications for intervention and treatment.
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss – This is the most common type and occurs when there is damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve. This damage can be caused by age, noise exposure, illnesses, injuries, or as a result of genetics. This kind is typically permanent, but hearing can be improved through hearing aids.
- Conductive Hearing Loss – When the outer or middle ear is blocked or damaged, sounds cannot reach the inner ear. This can be due to a buildup of earwax, fluid in the middle ear, or abnormalities in the ear structure. Unlike sensorineural, conductive hearing loss may be temporary and can often be corrected with medical treatment or minor surgery.
- Mixed Hearing Loss – As the name suggests, this is a combination of sensorineural and conductive hearing loss. There may be damage in the outer or middle ear, as well as problems in the inner ear or auditory nerve. Identifying mixed hearing loss often requires a more comprehensive audiological evaluation to determine the proper course of treatment.
Identifying the Cause of Hearing Loss
Hearing tests can identify if hearing loss is due to damage in the ear or other underlying conditions. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment and the best way to prevent further degradation. Common causes of sensorineural loss that affects a high percentage of the population include:
- Aging
- Exposure to loud noise
- Head trauma
- Illnesses
- Ototoxic medications, such as chemotherapy and diuretics
Take Steps to Protect Your Hearing
Age-related hearing loss is unavoidable and a natural part of getting older. However, exposure to loud noise can accelerate hearing loss. You should consider investing in hearing protection if you work or play in loud environments.
- Wear ear protection when exposed to any noise over 85 decibels
- Noise-canceling headphones are safer than turning up the volume to mask background noise
- Give your ears a break after being exposed to prolonged periods of noise
Schedule a Free Hearing Test
Seeking a hearing test is an essential step in maintaining optimal ear health. Hearing Health Connection offers free one-on-one hearing tests and evaluations at our locations throughout New Jersey. You can also take a free online hearing test in the comfort of your home. Be proactive in recognizing the signs, and don’t hesitate to schedule an appointment with a hearing care provider at a location near you. Your hearing is invaluable and deserves the best care.